Transportation pooled funds
The Transportation Pooled Fund (TPF) Program allows federal, state, and local agencies and other organizations to combine resources to support transportation research studies. A pooled fund study is intended to address a new area of planning, research or technology transfer or provide information that will complement or advance those areas. Since 2003, over $650 million has been used on TPF research. Currently, Minnesota is leading 74 active TPF studies and has completed 210 studies to date.
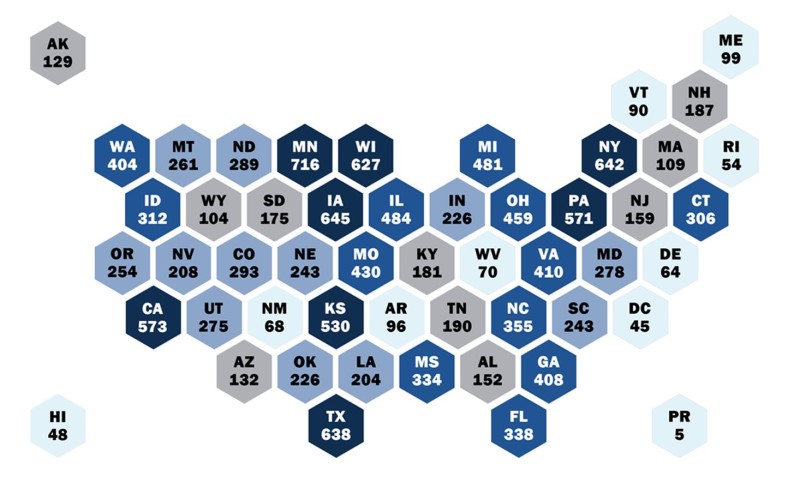
The number of TPF studies each U.S. state or territory has participated in.
Minnesota has participated in 716 studies.
MnDOT-led pooled fund programs/studies
Clear Roads
The Clear Roads research program brings together transportation professionals and researchers from around the country to drive innovation in the field of winter maintenance. By evaluating materials, equipment and methods in real-world conditions, the program identifies the most effective techniques and technologies to save agencies money, improve safety and increase efficiency.
National Partnership to Improve the Quality of Preventive Maintenance Treatment Construction & Data Collection Practices (PG Phase III)
This pooled-fund study will support state highway agencies (SHAs) and other Local Public Agencies (LPAs) by improving the application and quality of preventive maintenance (PM) on their pavements under live traffic conditions. The study will also provide guidance and funding to SHAs and LPAs in an effort to standardize or harmonize treatment strategies, address implementation efforts, and develop best construction practices utilizing their existing specifications or available AASHTO standards. For the study to be valuable, documentation of pretreatment pavement condition is critical along with monitoring of post treatment performance. The study will use established and proven data collection procedures such as those from the Long-Term Pavement Performance (LTPP) program to monitor the PM treatments. This data will be available to the public through an online system (e.g. LTPP InfoPave™ web portal).
Continuous Bituminous Pavement Stripping Assessment Through Non-destructive Testing
Stripping is a critical pavement subsurface distress affecting the performance and durability of asphalt pavement systems. The most challenging aspect of stripping is that it starts at the bottom or middle of bituminous layers and propagates upward. This makes it almost impossible to detect and quantify at early stages through visual inspections or traditional pavement forensic investigation tools. Fortunately, new, advanced, non-destructive evaluation (NDE) technologies are becoming increasingly accessible and suitable for solving complex pavement issues. The primary objective of the pooled-fund project is to develop a methodology for rapid and automatic detection of stripping in bituminous pavements using 3D-GPR and other NDE technologies.
Continuous Asphalt Mixture Compaction Assessment using Density Profiling System
It is well known that having adequate and uniform asphalt mixture compaction is critical for pavement life. Multiple studies have estimated that a 1% decrease in density can reduce pavement life by approximately 10%. Several state DOTs have evaluated a particular Ground-Penetrating Radar (GPR) DPS system, called the Rolling Density Meter (RDM), and got generally promising results. A calibration method for the RDM system has been developed and recommended. Additional research and improvements are still needed.
Enhancement to the Intelligent Construction Data Management System (Veta) and Implementation
Intelligent construction data collection systems such as geospatial systems, ground penetrating radar, and pavement smoothness profiles gather large quantities of data each day of production activities. Materials and construction personnel need integrated visualization and analysis systems to evaluate the large amount of data in near realtime and make decisions regarding acceptance.
National Accessibility Evaluation
This project has two main objectives. First, it will create a new, national accessibility dataset, accurate to the census-block-level, that can be used by partners in local transportation system evaluation, performance management, planning, and research efforts. Second, it will produce and publish a series of annual reports describing accessibility to jobs by driving and by transit in metropolitan areas across America.
National Road Research Alliance
The National Road Research Alliance (NRRA) pooled fund focuses on solving problems that impact road owners with an emphasis on customer needs. This pooled fund will help direct and complement the use of the MnROAD test track for local, regional and national research, technology transfer and implementation needs.
North/West Passage
Interstates 90 and 94 between Wisconsin and Washington (the "north/west passage") are major corridors for commercial and recreational travel. They are also subject to extreme winter weather conditions that pose significant operational and travel-related challenges in all the cooperating states. These states — Idaho, Minnesota, Montana, North Dakota, South Dakota, Washington, and Wyoming — are predominantly rural and face similar transportation issues related to traffic management, traveler information, and commercial vehicle operations. Recognizing the value of coordinated, cross-border collaboration for Intelligent Transportation Systems deployment to address these issues, Minnesota initiated a meeting in 2002 with representatives from each of the states within the corridor. The group established itself as a Transportation Pooled Fund in 2003. North/West Passage members contribute $25,000 or more annually to the pooled fund and are reimbursed for program travel. A work plan is developed and approved annually by the Steering Committee.
Find a full list of MnDOT TPF solicitations and studies
Other MnDOT pooled fund programs
Autonomous Maintenance Technology (AMT)
This study supports and promotes collaborative research efforts in the field of autonomous technologies in work zone applications to improve the safety and efficiency of workers on road construction. The participation of many transportation related agencies in this study furthers the cooperation in this industry, leading to improved future development of beneficial technologies and improved sharing of information and lessons learned, with cost savings for all participants.
Aurora
Aurora is an international program for advancing road weather information systems (RWIS) technology. Aurora and its members seek to implement advanced road weather information systems (RWIS) that fully integrate state-of-the-art roadway and weather forecasting technologies with coordinated, multi-agency weather monitoring infrastructures.
Bridge Element Deterioration for Midwest States
The objective of this pooled fund research was to pool bridge data from midwest DOTs related to element level deterioration, operation practices, maintenance activities, and historic design/construction details. This data provided the basis for researchers to determine deterioration curves.
Center for the Aging Infrastructure: Steel Bridge Research, Inspection, Training and Education Engineering Center - SBRITE
This project supports the Steel Bridge Research, Inspection, Training, and Education Engineering Center (S-BRITE Engineering Center) at Purdue University. This national center provides education, training, research, and engineering expertise to member states. Although the center is focused on highway bridges, it also supports stakeholders of steel railroad bridges, as well as steel ancillary structures, such as lighting towers and sign supports. The center contributes to improved asset management decisions for DOTs, FHWA, and other partners relative to existing steel bridge inventory.
Construction of Low-Cracking High-Performance Bridge Decks Incorporating New Technology
The purpose of this study is to implement new technologies in conjunction with low-cracking high-performance concrete bridge specifications to improve bridge deck life through reduction of cracking. The work involves cooperation between state departments of transportation (DOTs), material suppliers, contractors, and designers.
Develop and Support Transportation Performance Management Capacity Development Needs for State DOTs
The focus of this pooled-fund project will be to research and assess training and educational needs of contributing members, develop and deliver training, and to facilitate the sharing and retention of performance management best practices.
Development of an Integrated Unmanned Aerial Systems (UAS) Validation Center
This pooled-fund study proposes to develop the standards, protocols, and testing requirements that a given UAS must meet and demonstrate for a particular application. The current industry is unregulated with regard to establishing the required level of performance for UAS in civil engineering applications. The results of this study will be the development of the performance measures and validation criteria that agencies can use when making decisions about deployment of UAS in the context of civil engineering.
Development of Maintenance Decision Support System
To provide safe transportation to motorists, state transportation agencies in northern states must apply effective highway maintenance treatments appropriate to a wide range of winter and year-round conditions. Maintenance personnel must decide what treatments to apply, and when to apply them, based on their knowledge of current pavement conditions, current and forecast weather conditions, and available maintenance techniques and resources. In large part, the decisions are based upon prior experience of maintenance personnel and supervisors.
Enhanced Traffic Signal Performance Measures
This project addresses two needs that emerged from previous research. 1. Traffic Signal Data Logger Update: Update the data logger specification to provide secure file transfer, incorporate new enumerations that have emerged, and logging new connected vehicle messages. 2. Probe Data: Current probe data tools are focused on freeway data. There is a need to develop methodologies and tools for using high resolution vehicle trajectory data to compute traffic signal performance measures.
Evaluation of Lateral Pile Resistance Near MSE Walls at a Dedicated Wall Site - Phase 2
MnDOT and other states are interested in using abutment piles behind mechanically stabilized earth (MSE) walls rather than a soil slope. This should result in a more economical, simpler, and faster method of bridge construction. Previous testing by other states and BYU shows a significant decrease in lateral resistance and increases in reinforcement force as piles are placed closer to the MSE wall. Placing piles further from the wall increases bridge cost. Additional field testing at mock MSE abutment with single and group piles is necessary to define performance to provide guidance to designers.
Evaluation of Low Cost Safety Improvements
This project will evaluate the priority strategies from the NCHRP Report 500 Guidebooks, Guidance for Implementation of the AASHTO Strategic Highway Safety Plan. The safety effectiveness of many of the strategies in the guidebooks has not yet been rigorously evaluated. In order to achieve a national goal shared by the USDOT, AASHTO, and GHSA to reduce the fatality rate to 1.0 and save 9,000 lives annually by 2008, these strategies will need to be appropriately implemented. In this project, therefore, data will be collected and before-after safety effectiveness evaluations will be performed at sites where selected safety strategies are being implemented. A steering committee, comprised of pooled fund State DOT representatives, will provide guidance on the strategies selected for evaluation.
Exploring Non-Traditional Methods to Obtain Vehicle Volume and Class Data
The objective of this pooled fund project is to develop and deploy methods to obtain vehicle volume and classification data with passively collected data (by a traffic link system, for example). Volume data refers to the annual average daily traffic (AADT) for all vehicles (both passenger and trucks) covering all roadway functional classes with emphasis on minor arterials, collectors, and local roads. Passive volume data collection is also very desirable on high volume urban interstates as there is greater personal risk for collecting this data in person, and collection activities can disrupt normal traffic patterns.
High Occupancy Vehicle / Managed Use Lane
The goal of this study is to assemble regional, state, and local agencies, service providers, and FHWA to:
- Identify issues that are common among agencies that manage roadway lanes as a tool to reduce congestion and optimize facility usage.
- Suggest projects and initiatives to advance practice.
- Select and initiate projects intended to address identified issues.
- Identify recommendations and potential solutions.
- Disseminate results.
ENTERPRISE
Evaluating New Technologies for Roads Program Initiatives in Safety and Efficiency (ENTERPRISE) will develop and carry out a joint research program to develop, evaluate, and deploy ITS technologies. Each year, members contribute funds in support of ITS projects of mutual interest and develop an annual work plan. These projects typically involve private sector partners working with designated member agencies. Over time ENTERPRISE has grown into a multi-national consortium dedicated to the advancement of ITS. Its current partners include active ITS states from across the U.S., as well as Canadian and European agencies. ENTERPRISE provides a focus for coordinating ITS developments and for sharing results within and outside the program.
Midwest States Pooled Fund Crash Test Program
Specific research activities conducted by the Midwest Roadside Safety Facility (MwRSF) under this program include the design, analysis, testing, and evaluation of crashworthy structures, and the development of guidelines for the use, selection and placement of these structures. Sixteen states including Minnesota are currently participating in this program.
MnROAD Partnership With National Center for Asphalt Technology
The Minnesota Department of Transportation's road research facility, MnROAD, has partnered with the National Center for Asphalt Technologies in Auburn, Alabama to improve coordination of experiments and expand evaluation of pavement performance in both northern and southern climates, providing cost-effective solutions that can be implemented nationwide. Currently, a total of 17 states are sponsoring these projects. There are seven committed northern states including Colorado, Illinois, Michigan, Maryland, Minnesota, New York, and Wisconsin. The Foundation for Pavement Preservation and the National Center for Pavement Preservation are also active members.
Roadside Safety Research for MASH Implementation
In 2005, a consortium of states joined together to pool resources to identify and address common roadside safety research needs. Research activities include the design, analysis, testing and evaluation of roadside safety hardware such as bridge rails, guardrails, transitions, median barriers, work zone traffic control devices, terminals, and break away support structures. Together, they have committed over $2.5 million in research funding over a 10 year period to fund over 35 projects. The implementation of the AASHTO Manual for Assessing Safety Hardware (MASH) by State DOTs will necessitate the examination and evaluation of roadside safety hardware currently being used by the State DOTs. It is already known that some currently used roadside safety hardware will not meet MASH requirements.
Wildlife Vehicle Collision Reduction and Habitat Connectivity
Wildlife vehicle collisions (WVCs) have become an increasingly larger component of overall crashes nationally, while at the same time local populations of wildlife, both large and small, have suffered restrictions to their safe movement across roads. While there are several proven mitigation measures that significantly reduce WVCs, provide safe wildlife passage, and maintain habitat connectivity, there are many new technologies or improvements to old mitigation measures that may help reduce mitigation costs. This study explores these new technologies.
